IP Passthrough: Direct Connectivity for Teltonika devices
In the dynamic world of networking, achieving seamless and direct connectivity for critical devices isn't just a convenience. While NAT efficiently shares a single public IP address among countless devices, there are profound scenarios where a specific piece of equipment absolutely needs to directly "own" that public IP. This is precisely where IP passthrough emerges as a powerful option, offering a direct path to the internet.

This article will embark on a journey to unravel what is IP passthrough, explore the various IP passthrough modes, clarify the distinction between IP passthrough port vs MAC, and illuminate why this feature proves particularly useful when integrating Teltonika‘s connectivity devices into your infrastructure.
What is IP Passthrough? The Concept Explained
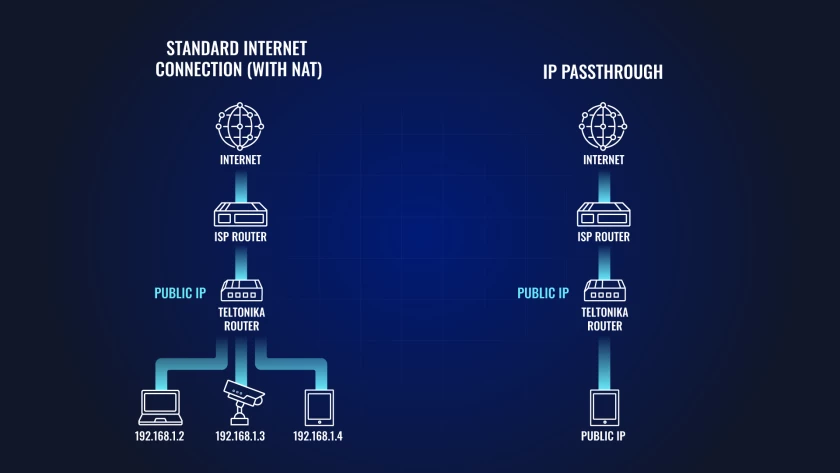
At its heart, IP passthrough is an ingenious networking function that grants a chosen device on your local network the privilege of directly receiving the public IP address assigned to your router by your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
Imagine it as giving that one device the direct internet connection, bypassing the router's usual NAT function. This means the designated equipment appears as if it's plugged straight into the network, rather than sitting behind another layer of network translation.
In essence, it's a method of bypassing the conventional NAT firewall for a single, designated device, giving it unfiltered access to the internet and allowing it to be directly addressed from the internet.
Why Direct Connectivity is Useful with Teltonika
Teltonika‘s networking devices, renowned for their ruggedness and versatility in industrial and enterprise-grade applications, often find their home in demanding environments where direct device connectivity isn't merely beneficial – it's absolutely critical.
Navigating the Demands of Industrial and Remote Environments
Consider, for instance, the intricate world of Industrial Automation (IIoT). Within factories, power grids, or water treatment facilities, devices like PLCs, sophisticated sensors, and robotic systems demand unwavering, real-time communication with central control units or cloud platforms. Direct connectivity here becomes the foundation for low-latency data flow and consistent operations in these mission-critical scenarios.
Similarly, in the rapidly evolving landscape of Smart Cities and Infrastructure, systems governing traffic management, intelligent streetlights, environmental monitoring stations, and public Wi-Fi hotspots necessitate constant, uninterrupted communication.
These geographically dispersed devices often require individual addressability for crucial monitoring, timely configuration updates, and robust data collection. Here, direct IP access significantly simplifies remote management, ensuring these vital public services remain operational and responsive around the clock.
Then there's the realm of Remote Monitoring and Surveillance. Security cameras perched in distant locations, remote access points, or specialized monitoring equipment at sprawling construction sites and agricultural facilities frequently demand instant access from a central command centre.
Furthermore, in Fleet Management and Transportation, vehicles with Teltonika routers for tracking, telemetry, and in-vehicle connectivity rely on stable, direct connections for seamless data synchronization, real-time GPS updates, and swift remote diagnostics. As vehicles traverse various cellular networks, direct IP can cultivate a more resilient and efficient data transfer experience.
Even in Retail and Point-of-Sale (PoS) Systems, while often less about outward internet exposure, specific PoS terminals or specialized retail hardware might require direct communication with external payment gateways or cloud-based inventory systems.
Here, the ability to avoid network complexities for these critical transactional points is highly valued, ensuring smooth and uninterrupted business operations.
Overcoming Network Complexities: The Practical Advantages
In these demanding contexts, the direct device connectivity facilitated by IP passthrough offers tangible advantages.
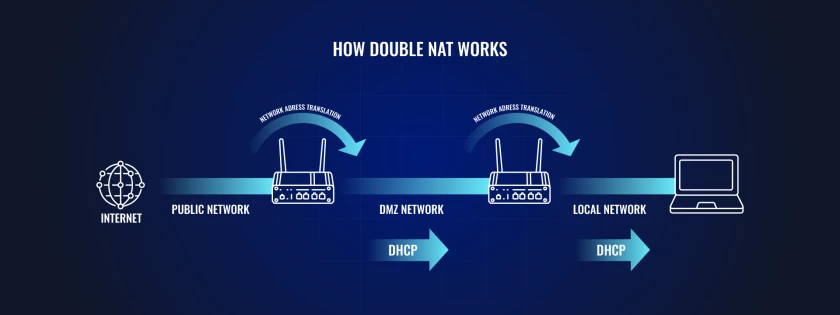
Eliminating Double NAT for Seamless Performance
One of the most immediate advantages offered by IP passthrough is its ability to eliminate the dreaded "Double NAT" scenario. This common challenge arises when an ISP-provided modem/router is combined with another router, for example, a Teltonika device.
This double layer of Network Address Translation can cripple performance for real-time applications and vital VPNs, leading to increased latency and connectivity issues. By allowing your Teltonika router to acquire the public IP directly, IP passthrough resolves these double NAT issues, paving the way for smoother, more predictable operation across your network.
Empowering Server Hosting and Services
Beyond preventing double NAT, IP passthrough dramatically simplifies the process of hosting servers and services directly from your local network.
For businesses or specialized applications that rely on dedicated servers – be it for web servers, FTP services, VPN endpoints, or CCTV surveillance systems – directly connected to a Teltonika router, IP passthrough grants immediate, unfiltered internet accessibility.
This eliminates the intricacies typically associated with external connections and port forwarding, making your services easily reachable by external users and applications.
Streamlining Remote Management and IoT Deployments
Crucially, direct IP connectivity delivers enhanced remote management capabilities, which are the very essence of many industrial IoT (IIoT) and M2M solutions. These deployments frequently hinge on reliable, consistent remote access to geographically dispersed devices.
With IP passthrough, a Teltonika router can directly expose a connected device to the internet, rendering remote monitoring, diagnostics, and control far more straightforward and robust.
This direct path minimizes points of failure and simplifies the architecture for large-scale IoT networks, ensuring critical data flows smoothly from edge devices to central platforms.
Exploring IP Passthrough Modes and Configuration
Understanding the various ways IP passthrough can be implemented is key to leveraging its full potential within your network. Teltonika‘s connectivity devices, like many advanced routers, offer different IP passthrough modes, designed to cater to multiple deployment scenarios.
Bridge Mode: The Direct Link
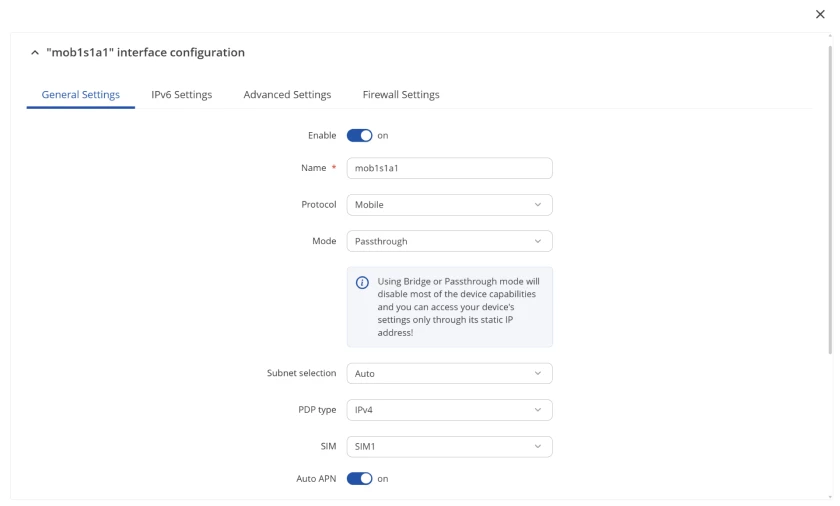
In its purest form, Bridge Mode (often simply referred to as "Passthrough Mode" in some contexts) transforms your Teltonika device into a direct link, forwarding the public IP address to a single connected device, which is often another router or an end device.
This mode is ideal when you want your Teltonika device to simply pass the public IP to a downstream router that will handle all subsequent network translation and routing.
A crucial point for Teltonika users when operating in this mode, particularly with mobile WANs, is its impact on router accessibility. If the connected client successfully acquires the public IP, the Teltonika router's WAN interface typically will not hold an IP address itself, meaning it won't be directly accessible from the WAN side. This requires management from the router's LAN side.
For more detailed troubleshooting and common issues specific to Teltonika's mobile bridge mode, the official Teltonika Wiki offers a straighforward resource: Mobile Bridge mode troubleshooting.
NAT Mode: The Standard Gateway
While this article primarily focuses on scenarios where NAT is bypassed, it's essential to understand NAT Mode as the foundational, standard operational mode for most routers.
In this configuration, your Teltonika router acts as the primary gateway for your local network, efficiently translating a single public IP address from your ISP into multiple private IP addresses for all your connected devices.
In this common and default setup, the router's WebUI and RMS are readily accessible from both the LAN and, with appropriate firewall rules, the WAN side, providing straightforward and comprehensive management capabilities.
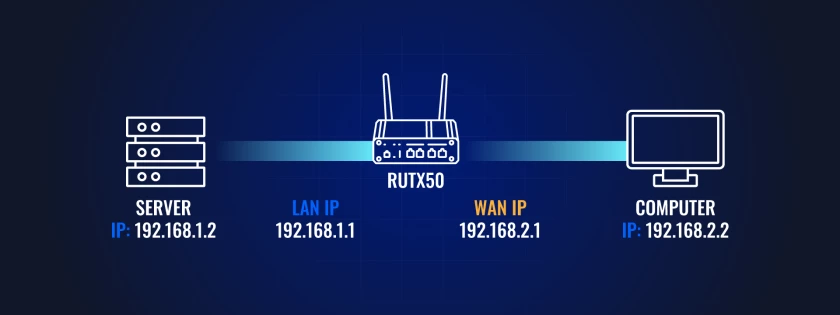
One-to-One NAT: Direct IP Mapping
Though not strictly identical to true IP passthrough, One-to-One NAT offers a related approach to directness for a specific device. In this mode, a single private IP address on your local network is permanently and exclusively mapped to a single public IP address provided by your ISP.
This creates a dedicated public mapping for that device, allowing it to be directly addressed from the internet without sharing the public IP with other devices via standard NAT.
While the underlying mechanism still involves Network Address Translation, it does so in a dedicated fashion, providing a direct link. It remains paramount to consult the specific Teltonika device's detailed documentation to fully grasp the available passthrough mode options and their precise configuration requirements.
For a deeper technical dive into the nuances of these mobile modes and their implications for Teltonika devices, the Teltonika Community forum provides an excellent resource, specifically discussing the differences in behavior for NAT, Bridge, and Passthrough modes).
Precision Control: IP Passthrough via MAC Address
When configuring IP passthrough, you have two primary options:
- Do not specify a MAC address: The public IP will be assigned to the very first device that connects to the router. This method is convenient if you only have one device to connect.
- Specify IP Passthrough MAC Address: This stands as the more prevalent, robust, and generally recommended method. Here, you meticulously enter the Media Access Control (MAC) address – the unique hardware identifier – of the specific device that you intend to receive the public IP.
This approach offers superior control and assurance that only the intended device secures the direct internet connection, irrespective of which physical port it's connected to. Importantly, Teltonika's connectivity devices frequently leverage this MAC address-based configuration for IP passthrough, providing granular and precise control over your network.
This method also ensures that even if the device is moved to another port, it retains its direct public IP.
Configuring IP Passthrough on Teltonika Devices: A Step-by-Step Guide
While the exact steps might exhibit minor variations depending on your specific Teltonika router model and its firmware version, the general configuration process typically involves a straightforward sequence:
- Accessing the Web UI: Begin by securely logging into your Teltonika device's intuitive web administration interface using your preferred web browser.
- Navigating to Network Settings: Proceed to locate the dedicated WAN or Internet settings section, as IP passthrough pertains to how your device manages its external connection.
- Enabling Passthrough: Within these settings, meticulously search for options explicitly related to "IP Passthrough," "Bridge Mode," or in some cases, "DMZ" when targeting a single specific device. The exact wording will depend on your router's firmware.
- Specifying the Target Device: This crucial step typically requires you to accurately enter the MAC address of the device slated to receive the public IP. Ensure you have the correct MAC address for the target device (e.g., your secondary router, server, or industrial controller).
- Saving and Applying: Conclude by saving your carefully configured changes and allowing the device to perform a necessary reboot, if prompted. This reboot ensures the new network settings are fully applied.
For specific, detailed configuration instructions the official Teltonika Wiki provides comprehensive manuals, such as this one.
A Crucial Security Caveat
While the utility of IP passthrough is undeniable, it is paramount to remember that the device receiving the public IP address becomes directly exposed to the vast and often volatile internet.
Consequently, it is essential to ensure that this device is fortified with its own robust firewall, possesses the latest security patches, and implements all necessary security measures to diligently protect against the ever-present spectrum of cyber threats.
Empowering Your Network with Teltonika IP Passthrough
IP passthrough stands as a remarkably powerful feature, designed to provide direct internet connectivity for critical devices, bypassing the complexities of traditional NAT. For users of Teltonika's connectivity devices, understanding and leveraging IP passthrough modes and MAC-based configuration unlocks significant advantages.
This essential functionality empowers unparalleled network performance, simplifies server hosting, enhances remote management, and streamlines complex IoT deployments. By harnessing IP passthrough responsibly, you ensure optimal, resilient connectivity for your most vital applications. Teltonika's commitment to versatile and secure networking makes IP passthrough an invaluable tool for modern industrial and enterprise solutions.