Beyond Signal Bars: Understanding RSSI, RSRP, SINR & Other Key Metrics
#2025, #remotemanagement, #connectivity, #4g, #3g, #5g, #news
Signal bars may seem straightforward—but do they tell the whole story? In the IoT world, simply being connected isn’t enough. Understanding the quality of that connection is just as important. That’s why Teltonika goes beyond building industrial-grade networking devices—we equip you with the tools and insights to get the most out of them. And it all starts with understanding mobile signal metrics.
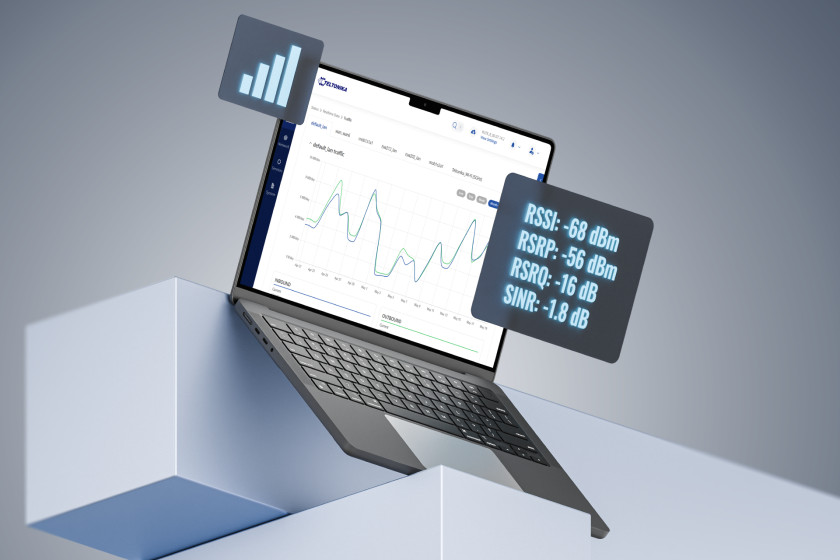
Your connection depends on several factors—your router, network provider, and physical environment all play a role. Even if your device shows a strong RSSI value, like –68 dBm, it doesn’t always mean your connection will perform well. Why not? Because other elements—such as tower congestion, weather conditions, and distance from the cell tower—can still degrade performance. That’s why we don’t rely solely on signal bars or a single metric to evaluate connection quality.
We combine RSSI, RSRP, RSRQ, and SINR to give a complete view of your connection quality. Only by looking at the full picture can you truly understand and manage performance. For professionals, accuracy matters. Let’s break it down by generation.
2G: RSSI LEVEL MEASURING
While RSSI offers a limited view of signal quality in modern networks, it remains the primary and often only available indicator in 2G systems. It reflects the power level of the cellular signal received by your modem from the nearest cell tower, measured in dBm. This gives a general idea of how strong the signal is—but not how clean or usable it is.
Open WebUI: Status → Network → Mobile
If your device is registered to RMS and online, you can use the WebUI icon within RMS to launch the interface remotely.
While RSSI provides a basic overview, it doesn’t reflect signal quality, such as noise, interference, or network congestion. Still, in 2G systems where advanced metrics aren't available, RSSI remains your main reference point for assessing connectivity.
If your operations depend on consistent 2G coverage, aim for the best mobile signal strength above -70 dBm whenever possible. Check the tab below to understand what's your signal strength.

3G: COMBINING RSSI, EC/IO and RSCP
3G networks use three indicators: RSSI, Ec/Io, RSCP. RSSI works similarly to 2G, but Ec/Io adds signal quality by measuring interference. RSCP tells you how strong the signal is after it's been processed by the network.
To check the 3G signal strength values of your RUT device, log in to your router's WebUI through browser and go to:
Status -> Network -> Mobile
If your device is registered to RMS and online, you can use the WebUI icon within RMS to launch the interface remotely.
When optimizing a 3G setup, don’t rely solely on Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI). A strong RSCP combined with a clean Ec/Io ensures low latency, stable connections, and consistent data throughput. Check the tab below to understand a full picture of your connection.

4G and 5G: RSSI, RSRP, RSRQ, AND SINR MEASURES
For 4G and 5G, signal strength and quality are measured using four main indicators. RSSI shows total 4G and 5G signal strength but includes noise. RSRP measures the strength of the useful signal. RSRQ shows how clean the signal is, like Ec/Io in 3G. SINR compares your signal to any interference—higher SINR means faster, more stable internet.
To check your router's 4G/5G signal. Log in to your router's WebUI and go to:
Status -> Network -> Mobile
If your device is registered to RMS and online, you can use the WebUI icon within RMS to launch the interface remotely.
For example:
Your 4G/5G router might show.
RSSI: –68 dBm
RSRP: –56 dBm
RSRQ: –16 dB
SINR: –1.8 dB
At a glance, RSSI might seem decent—but SINR and RSRQ suggest poor signal quality. This can be caused by distance from the tower or signal interference. Review the table below for a complete overview of your connection.

OTHER METHODS TO CHECK SIGNAL QUALITY
Router LEDs: check the Signal Strength LEDs on the router's front panel. While these do not show exact values, they represent RSSI strength in bars, much like a mobile phone.
Command Line Interface: For detailed signal diagnostics, use gsmctl commands via CLI. A command interact directly with the router's modem, translating to AT commands and returning readable results—ideal for checking your signal for automation, remote monitoring, or headless setups.
Access CLI from System → Maintenance → CLI.
You should see a window as shown below where you need to login with default administrator username (root) and a password.

Once you're logged in, type the following command:
gsmctl -q
This will display a detailed table showing your signal strength and quality metrics.
WHY UNDERSTANDING SIGNAL MATTERS
Understanding your signal metrics, is more than a technical detail—it’s critical for reliable, long-term operations. Signal drops, interference, and slow speeds can compromise your operation success.
With Teltonika devices, you can monitor these values directly from the WebUI or Remote Management System (RMS). This means you can verify the best mobile signal strength without leaving your desk—or optimise installations onsite with real-time feedback.
GENERAL TIPS ON IMPROVING SIGNAL

✔️Place your router and antenna where the signal is strongest and least obstructed—typically near a window or higher up. Avoid physical barriers like thick walls, trees, or buildings that could interfere with the signal.
✔️Ensure antenna connections on your router are tight and secure—loose connectors can significantly reduce signal quality.
✔️If you're still experiencing poor connectivity after optimizing placement and hardware, consider switching to a provider with better network coverage in your area.
THE IMPORTANCE OF STRENGTH
From smart cities to industrial and automation, reliable connectivity starts with understanding your signal metrics. Knowing what cellular signal metrics truly mean, helps you make informed decisions and ensures your setup performs at its best.
At Teltonika, we go beyond hardware—we empower you with the insights and tools to turn every connection into a success. Ready to get started on your next project? Click the “Contact us” button below—we’re here to help.


